Index
Chromasomal Mutations
Genetic Mutations
Chromasomal Mutations
Occurs in the chromosomes and are caused in a couple of different ways

Deletion
Occurs when one Amino acid is deleted from the sequence.

Inversion
When a chromosome is mutated when a nucleic acid is inverted or switched with another
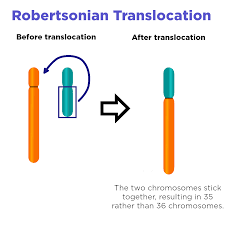
Translocation
When part of one chromosome binds to another.
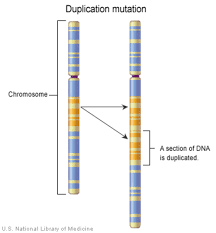
Duplication
When part of a chromosome is duplicated
DNA Mutations
- Deletion, nitrogenase base is deleted –Frame Shift Mutation
- Insertion, A nitrogenase base is added –Frame Shift Mutation
- Substitution
Vocabulary
- Frame Shift Mutation – Mutation that causes all procceding dna NB to be shifted down or up. this causes a frameshift.
- Nondijusction mutation – A mutation caused when 2 homologous chromasomes are not correctly seperated.
- Silent Mutation – A mutation that changes a NB but does not change the resulting Nuclaic Acid and therefore protein produced.
- Sematic Cells – A cell/s that are strictly body cells and do body things.
- Germ Cells, Gametes, Sex Cells – cells dealing in reproduction
- Germ Mutations- Mutations that affect sex cells causing offspring to inherit un intended mutations
- mutagens – factors that lead to a mutation
- Gene Mutation – Mutaion in the genes, usually during DNA replication or S phase
- Point Mutations – Mutations that do not cause a framshift but rather replace a nucelotide
- Meiosis – Cell Cycle for Sex Cells
- Misense Mutation – Muations that result in a different nucleotide.
Additional
- Most organisms tend to have 2 sets of chrmasomes but some have more, this is called Polyploidy when an organism has more than 2 sets of chromasomes
- Anepology is when an organism has the common 2 sets. This is what occurs in humans. -Humans have 46 pairs or 23 chromasomes from each parent.
BIology Notes 3.0
